Ohio’s climate is generally too cold to support the growth of palm trees. The state primarily experiences a humid continental climate, with some southern areas featuring a humid subtropical climate.
Summers in Ohio are characterized by heat and humidity, with average July temperatures ranging from 72 to 76°F (22 to 24°C). In contrast, winters tend to be cool to cold, with average January temperatures spanning from 25 to 31°F (-3°C to -1°C).
Ohio typically receives an annual snowfall ranging from 24 inches (61 cm) to 56.3 inches (143 cm). Occasionally, the state faces challenges such as tornadoes, snowstorms, and even earthquakes.
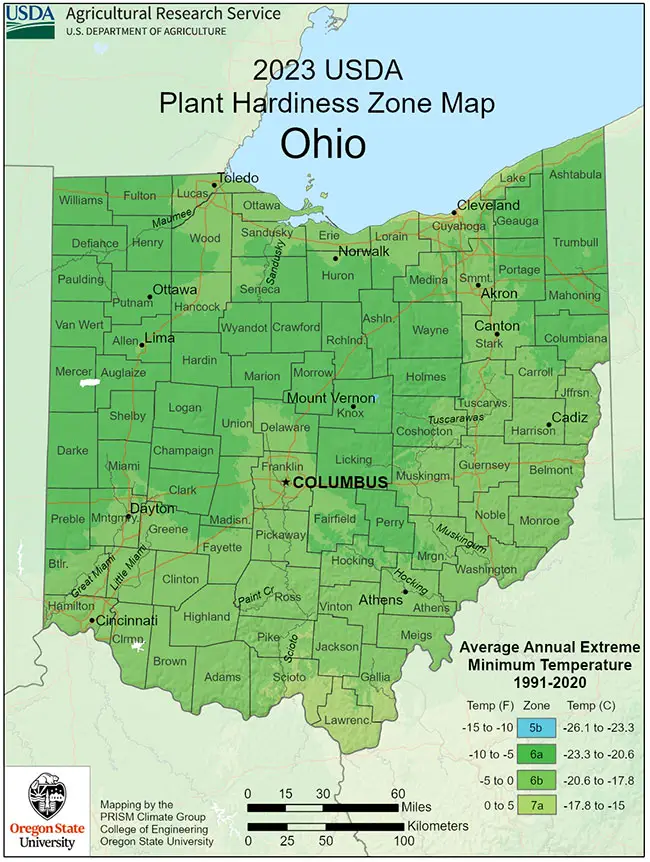
The highest temperature ever recorded in Ohio reached 113°F (45°C), while the lowest plummeted to –39°F (–39°C). Ohio’s USDA hardiness zones range from 5b to 6b.
Growing Palm Trees in Ohio
When examining the Ohio hardiness map, it becomes evident that zone 7 is virtually absent. Given that all other zones in Ohio are generally too cold to support palm tree growth successfully, a practical approach would involve cultivating palms indoors in containers and moving them outdoors during the warmer summer months.
This strategy can help protect palm trees from Ohio’s harsh winters and provide them with a more suitable environment for growth. Here are great indoor palms:
- Areca Palm Tree – Zones 9a – 11 (20 to 25 F)
- Chinese Fan Palm Tree – Zones 8a – 11 (10 to 15 F)
- Kentia Palm Tree – Zones 9b – 11 (25 to 30 F)
- Lady Palm Tree – Zones 8b – 11 (15 to 20 F)
More Palm Trees»
Major Cities in Ohio
Akron – Hardiness Zone 6b
Canton – Hardiness Zone 6a
Cincinnati – Hardiness Zone 6a
Cleveland – Hardiness Zone 6a
Columbus – Hardiness Zone 5b
Dayton – Hardiness Zone 5b
Lima – Hardiness Zone 5b
Parma – Hardiness Zone 6a
Toledo – Hardiness Zone 6a
Youngstown Hardiness Zone 5b
Zanesville – Hardiness Zone 5b

43730. What is the growing zone ?